Stay up to date with our recent products
Web Menu
Product Search
Exit Menu
Recycled Polyamide: A Step Toward Sustainable Innovation
Introduction
Polyamide, more commonly known as nylon, has been a cornerstone material in textiles, engineering plastics, and consumer goods since its invention in the 1930s. Strong, lightweight, and versatile, it is widely used in fashion, automotive, sports equipment, and industrial applications. However, conventional polyamide is derived from petrochemicals, making its production resource-intensive and environmentally taxing.
Recycled polyamide offers a more sustainable alternative, aligning with the global shift toward circular economy principles. By reclaiming and reprocessing nylon waste, manufacturers reduce dependence on virgin fossil resources, cut carbon emissions, and minimize landfill accumulation.
What Is Recycled Polyamide?
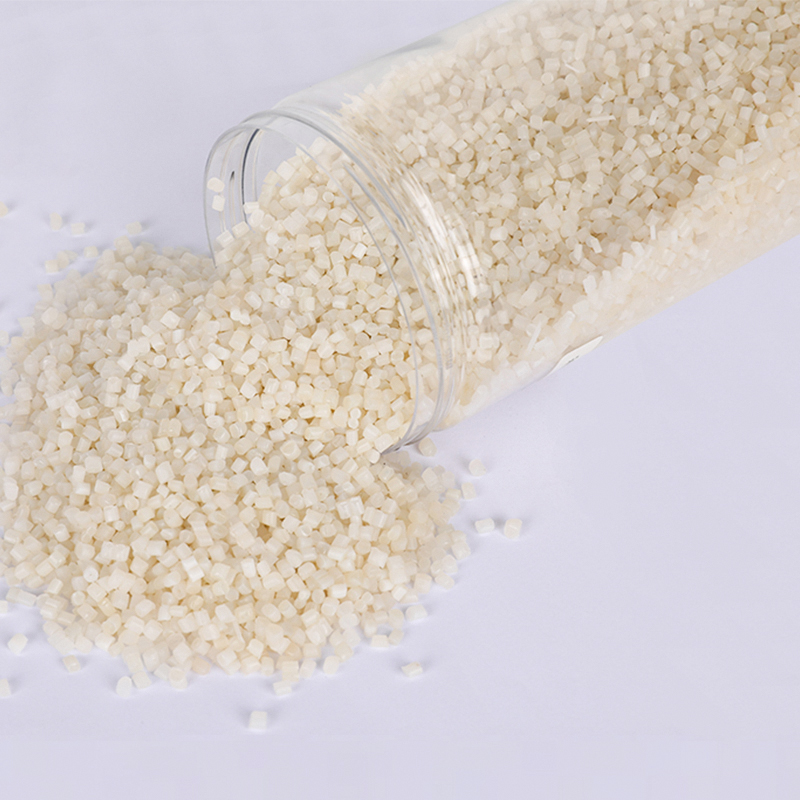
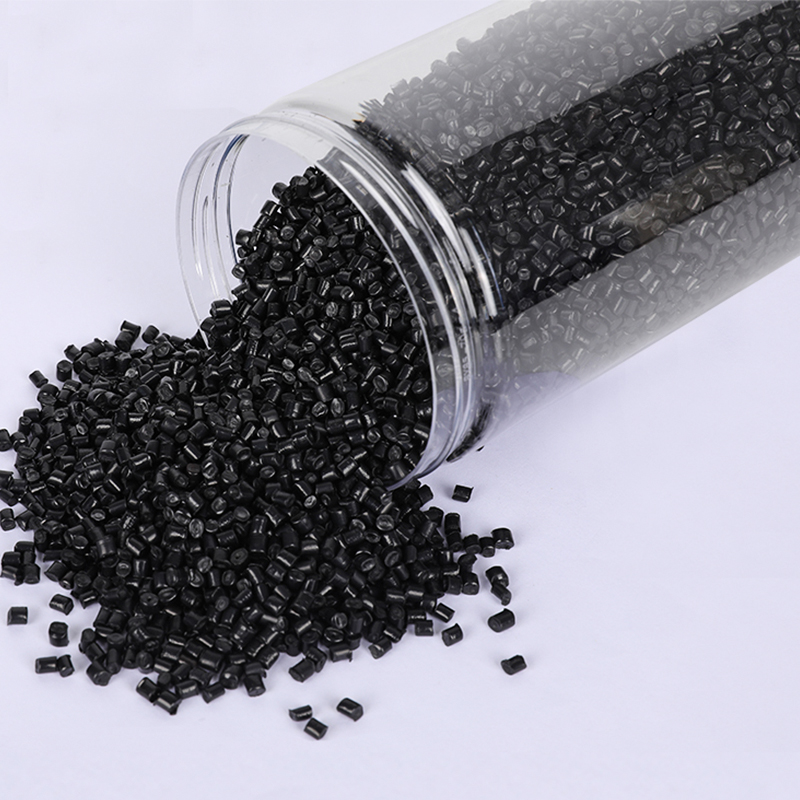
Recycled polyamide is produced by recovering post-industrial or post-consumer nylon waste and converting it back into usable fibers or granules. Common sources include:
Pre-consumer waste: Excess fibers, trimmings, or defective goods from manufacturing.
Post-consumer waste: Discarded fishing nets, carpets, and clothing.
Industrial waste: Nylon-based plastics and engineering components.
Unlike downcycling, where materials lose quality after recycling, advanced technologies allow polyamide to be regenerated to nearly the same performance level as virgin nylon.
Production Process of Recycled Polyamide
The recycling process can vary, but typically involves these steps:
Collection and Sorting – Nylon waste is gathered and separated from other materials.
Cleaning and Preparation – Contaminants, dyes, and coatings are removed.
Mechanical or Chemical Recycling:
Mechanical recycling grinds and melts nylon waste into granules for re-extrusion.
Chemical recycling breaks polymers into monomers, which are purified and repolymerized into virgin-quality polyamide.
Extrusion and Spinning – The recycled material is transformed into fibers, fabrics, or molded components.
Benefits of Recycled Polyamide
1. Environmental Impact
Reduces reliance on fossil fuels.
Lowers greenhouse gas emissions compared to virgin nylon.
Diverts waste from landfills and oceans.
2. Performance Retention
Comparable strength, elasticity, and durability to virgin polyamide.
Resistant to wear and abrasion, making it suitable for demanding applications.
3. Circular Economy Contribution
Encourages resource efficiency.
Supports closed-loop recycling systems in textiles and plastics.
Applications of Recycled Polyamide
Fashion and Textiles
Sportswear, swimwear, and hosiery.
Sustainable fashion brands use recycled nylon to reduce their footprint.
Automotive Industry
Lightweight components, airbags, and seat fabrics.
Industrial Uses
Ropes, nets, and protective gear.
Technical fabrics for aerospace and defense.
Consumer Goods
Footwear, backpacks, and accessories.
Eco-conscious alternatives in everyday products.
Challenges and Future Outlook
While recycled polyamide shows enormous promise, challenges remain:
Cost: Recycling technologies are more expensive than producing virgin nylon.
Collection systems: Efficient waste recovery infrastructure is still developing.
Market demand: Broader consumer awareness and adoption are needed.
Despite these challenges, innovation continues to accelerate. With increasing regulations, sustainable fashion commitments, and advancements in chemical recycling, recycled polyamide is poised to play a central role in reducing the environmental footprint of plastics and textiles.
Conclusion
Recycled polyamide represents a powerful step toward a sustainable future. By turning waste into valuable raw material, it reduces environmental harm while maintaining the high performance of traditional nylon. As industries and consumers increasingly embrace circular solutions, recycled polyamide will be at the forefront of innovation in fashion, manufacturing, and beyond.
As China PCR Recycled Plastic Granules Factory, We always adhere to the experience and philosophy of "keeping up with the times, constantly innovating, developing efficiently, and cooperating for mutual benefit"

Address: No.11, Wangzhuang Section, Provincial Road 01, Daqiao New Area, Economic Development Zone, Haiyan County, Jiaxing City, Zhejiang Province, China
Phone: +86-18058285678
Fax: +86-0573-86868101
E-mail: [email protected]
SUNRISE GROUP(Overseas Exclusive Agent)
www.sunrisechemical.com
2024 ICIS Global Chemical Distributor Top 8
Export Sales Manager:Helen Zhang
Mob/Whatsapp: +86 19883063465
Email: [email protected]
Copyright © Jiaxing Anyiju Plastic Industry Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved

 简体中文
简体中文 English
English