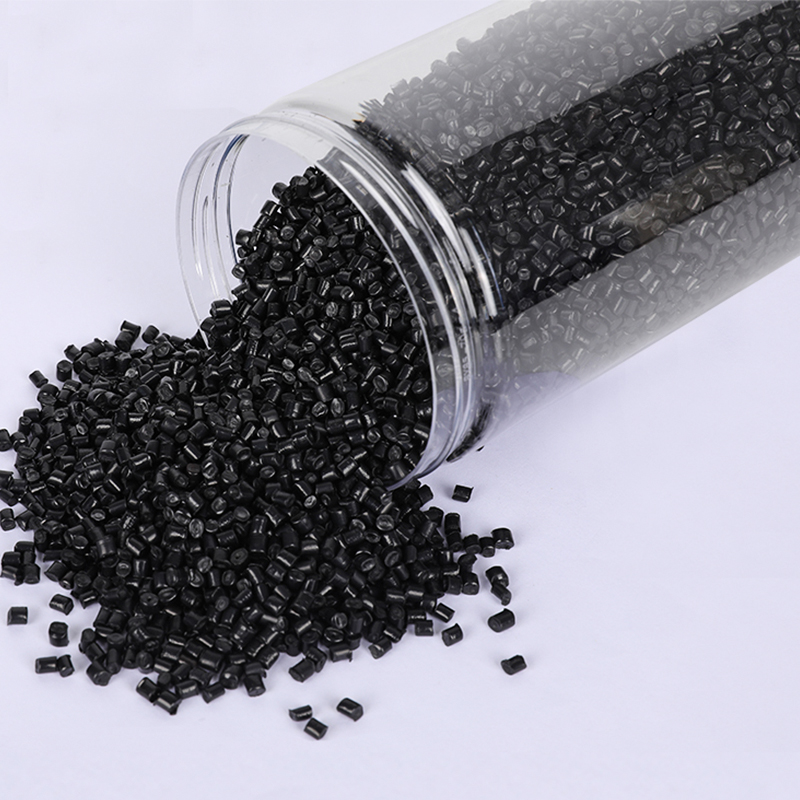
Stay up to date with our recent products
Web Menu
Product Search
Exit Menu
Understanding the Chemistry and Microstructure of ABS Resin to Enhance Its Performance in Industrial Applications
ABS resin stands out among synthetic plastics due to its unique chemical composition and versatile physical properties. At the heart of ABS resin’s performance lies its nature as a terpolymer, made up of three distinct monomers: acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene. Each component brings specific qualities that, when combined, result in a material with remarkable toughness, heat resistance, and chemical stability. Understanding how these elements interact on a molecular level helps manufacturers and users appreciate why ABS resin is highly valued across numerous applications.
The acrylonitrile portion of ABS resin contributes mainly to chemical resistance and thermal stability. It forms a rigid, polar segment that helps the material withstand exposure to oils, acids, and various solvents without degrading. This rigidity also enhances the resin’s resistance to high temperatures, making it suitable for products requiring sustained heat exposure. Meanwhile, the butadiene component acts as an impact modifier. Its rubbery nature provides the flexibility and toughness that prevent the material from cracking under sudden shocks or stresses, a critical factor for durability in many demanding settings.
Styrene in ABS resin imparts processability and aesthetic qualities. It offers a glossy, smooth surface finish, which is why products made from ABS often have a visually appealing look straight out of the mold. Styrene also allows easy coloration and painting, which is essential for applications where appearance matters, such as consumer electronics or automotive trim parts. The balance of styrene’s rigidity and butadiene’s elasticity results in a composite that can be precisely engineered for different performance needs by adjusting their ratios during production.
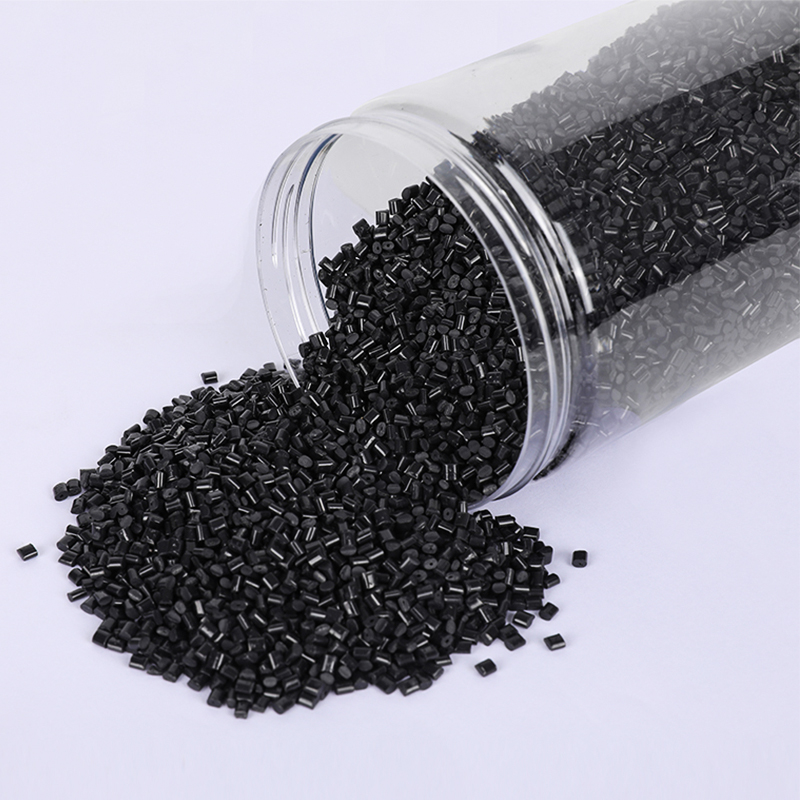

The microstructure of ABS resin reveals a phase-separated morphology, where rubbery butadiene particles are dispersed in a rigid styrene-acrylonitrile matrix. This two-phase structure is key to its impact resistance. When a force hits the material, the butadiene domains absorb and dissipate energy, reducing the chance of cracks forming. Manufacturers leverage this understanding to optimize ABS grades for specific mechanical properties, adjusting particle size and distribution to meet rigorous standards for toughness or flexibility.
ABS resin’s molecular design also facilitates various secondary processing techniques that add value to final products. Surface treatments like metal spraying and electroplating rely on the resin’s ability to maintain dimensional stability and adhesion during such processes. This adaptability is a direct outcome of the interplay between its chemical composition and microstructure, allowing customers to create high-quality, customized components without compromising durability or finish quality.
Adjusting the acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene content can tailor ABS resin to specific performance criteria. Increasing acrylonitrile enhances chemical resistance but reduces flexibility, while more butadiene boosts impact strength at the expense of stiffness. This tunability enables manufacturers to supply a broad spectrum of ABS materials suited to various sectors, from rugged automotive parts to lightweight consumer devices. Such flexibility underscores ABS resin’s status as a workhorse plastic with remarkable versatility.
Choosing the right ABS resin grade demands insight into these chemical and structural aspects. As a trusted manufacturer and supplier, we offer expertly formulated ABS variants that balance toughness, heat resistance, and finish quality. Understanding the science behind ABS resin empowers buyers to select materials that perfectly align with their product’s functional and aesthetic requirements, ultimately improving performance and customer satisfaction.
ABS resin’s sophisticated chemistry and microstructure form the foundation of its success in multiple applications. The synergy of acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene creates a plastic that is not only strong and heat-resistant but also easy to process and finish. This blend of qualities makes ABS resin an ideal choice for manufacturers looking for reliable, high-performance materials that deliver consistent results.
As China PCR Recycled Plastic Granules Factory, We always adhere to the experience and philosophy of "keeping up with the times, constantly innovating, developing efficiently, and cooperating for mutual benefit"

Address: No.11, Wangzhuang Section, Provincial Road 01, Daqiao New Area, Economic Development Zone, Haiyan County, Jiaxing City, Zhejiang Province, China
Phone: +86-18058285678
Fax: +86-0573-86868101
E-mail: [email protected]
SUNRISE GROUP(Overseas Exclusive Agent)
www.sunrisechemical.com
2024 ICIS Global Chemical Distributor Top 8
Export Sales Manager:Helen Zhang
Mob/Whatsapp: +86 19883063465
Email: [email protected]
Copyright © Jiaxing Anyiju Plastic Industry Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved

 简体中文
简体中文 English
English